Table of Contents
In this article, you’ll learn about What is Linux? Evolution, Advantages, Disadvantages, Structure and Architecture.
- Linux is a UNIX-base operating system.
- Its original creator was a Finnish student name Linus Torvalds. In 1991 he announced the creation of a new core operating system that he had named Linux.
- Its ‘open source’, belongs to nobody, and is free to download and use.
- Linux is free to use and install.
- It is more reliable than almost all other systems, running for many months and even years without a reboot being necessary.
- Any changes to it are open for all and is rapidly gaining in popularity worldwide, particularly among those seeking an alternative to Windows.
Evolution of Linux OS
The Linux OS was developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, which sprouted as an idea to improve the UNIX OS. He suggested improvements but was rejected by UNIX designers. Therefore, he thought of launching an OS, designed in a way that could be modified by its users.
Nowadays, Linux is the fastest-growing OS. It is used from phones to supercomputers by almost all major hardware devices.
Advantages of Linux
- Open source: Linux is an Open source operating systems. You can easily get the source code for linux and edit it to develop your personal operating system.
- Low cost: No need to spend time and money to obtain license since Linux and its software’s come with General Public License.
- Stability: There is no need to reboot the Linux system to maintain performance levels. Rarely it freeze up or slow down.
- Flexibility: Linux can be configured in detail and significant customization is possible without modifying the source code.
- Multitasking: Linux is a multitasking operating system. It can handle many things at the same time.
- Security: Linux is one of the most secure operating systems. Since the source code is visible, ‘backdoors’ are easily spotted
- Free software: A huge amount of free open source software has been developed for it
- Virus resistant: It is very resistant to spyware, adware and viruses.
- Wider choice: There is a large number of Linux distributions which gives you a wider choice like RHEL, Fedora, Mandreeva etc.
Disadvantages of Linux
- It is not very user-friendly. So, it may be confusing for beginners.
- It has small peripheral hardware drivers as compared to windows.
Different flavors of linux
Linux comes in many different guises. The basic system is the same, but the look and feel and the subsystems around it are different. Each version is produced by a different organisation with it’s own ethos and aims. Some flavours of Linux are as follows:
- Ubuntu
- Linux Mint
- Debian
- Fedora
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- SUSE Linux Enterprise
- Mandriva
- Arch Linux
- Slackware Linux
- Puppy Linux
- Linux kali / stratrack
Structure Of Linux Operating System
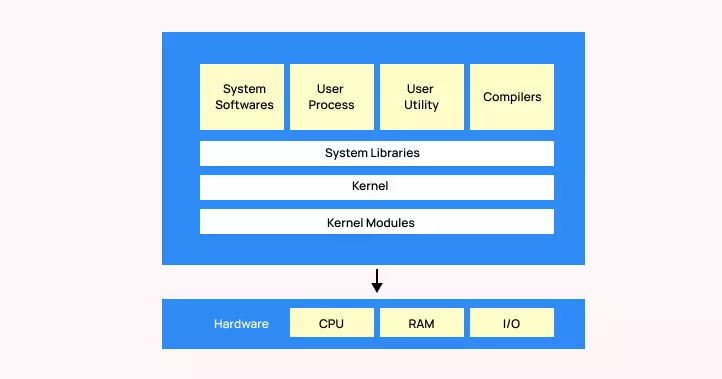
- Kernel: Kernel is the core of the Linux based operating system. It virtualizes the common hardware resources of the computer to provide each process with its virtual resources. This makes the process seem as if it is the sole process running on the machine. The kernel is also responsible for preventing and mitigating conflicts between different processes. Different types of the kernel are:
- Monolithic Kernel
- Hybrid kernels
- Exo kernels
- Micro kernels
- System Library − System libraries are special functions or programs using which application programs or system utilities accesses Kernel’s features. These libraries implement most of the functionalities of the operating system and do not requires kernel module’s code access rights.
- System Utility − System Utility programs are responsible to do specialized, individual level tasks.
Architecture of Linux

The architecture of a Linux System consists of the following layers
- Hardware layer − Hardware consists of all peripheral devices (RAM/ HDD/ CPU etc).
- Kernel − It is the core component of Operating System, interacts directly with hardware, provides low level services to upper layer components.
- Shell − An interface to kernel, hiding complexity of kernel’s functions from users. The shell takes commands from the user and executes kernel’s functions.
- Utilities − Utility programs that provide the user most of the functionalities of an operating systems.
Who uses Linux?
You probably already use Linux, whether you know it or not. Depending on which user survey you look at, between one- and two-thirds of the webpages on the Internet are generated by servers running Linux.
Companies and individuals choose Linux for their servers because it’s secure, flexible, and you can receive excellent support from a large community of users, in addition to companies like Canonical, SUSE, and Red Hat, each of which offer commercial support.
Many devices you probably own, such as Android phones and tablets and Chromebooks, digital storage devices, personal video recorders, cameras, wearables, and more, also run Linux. Your car has Linux running under the hood. Even Microsoft Windows features Linux components, as part of the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
