Bubble sort is based on the idea of repeatedly comparing pairs of adjacent elements and then swapping their positions if they exist in the wrong order.
Assume that A[] is an unsorted array of n elements. This array needs to be sorted in ascending order. The pseudo code is as follows:
void bubble_sort( int A[ ], int n ) {
int temp;
for(int k = 0; k< n-1; k++) {
// (n-k-1) is for ignoring comparisons of elements which have already been compared in earlier iterations
for(int i = 0; i < n-k-1; i++) {
if(A[ i ] > A[ i+1] ) {
// here swapping of positions is being done.
temp = A[ i ];
A[ i ] = A[ i+1 ];
A[ i + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}Lets try to understand the pseudo code with an example: A [ ] = { 7, 4, 5, 2}
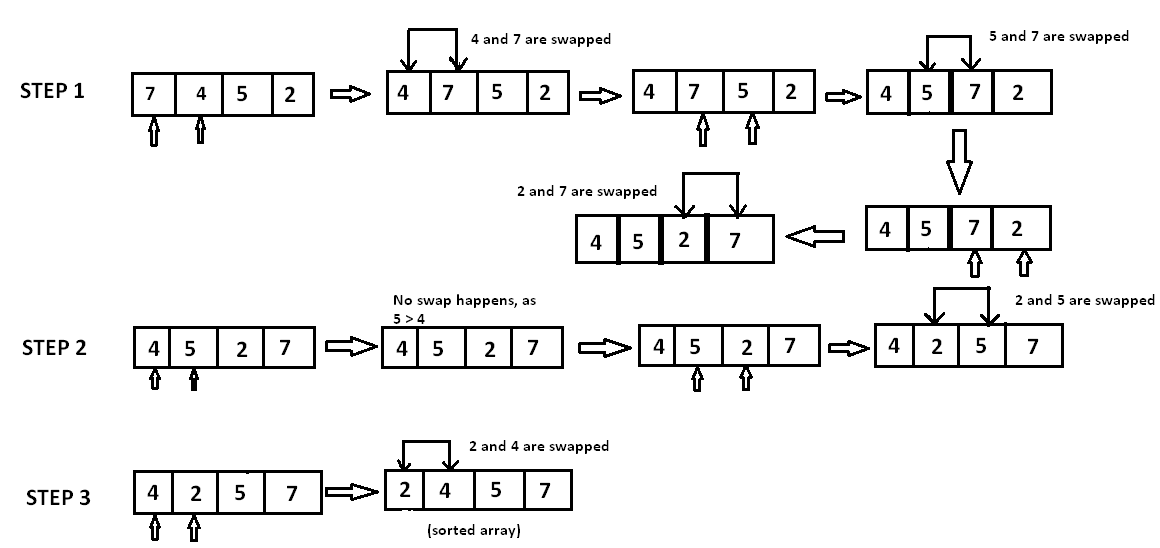
In step 1, 7 is compared with 4. Since 7>4, 7 is moved ahead of 4. Since all the other elements are of a lesser value than 7, 7 is moved to the end of the array.
Now the array is A[]={4,5,2,7}.
In step 2, 4 is compared with 5. Since 5>4 and both 4 and 5 are in ascending order, these elements are not swapped. However, when 5 is compared with 2, 5>2 and these elements are in descending order. Therefore, 5 and 2 are swapped.
Now the array is A[]={4,2,5,7}.
In step 3, the element 4 is compared with 2. Since 4>2 and the elements are in descending order, 4 and 2 are swapped.
The sorted array is A[]={2,4,5,7}.
Complexity:
The complexity of bubble sort is O(n2) in both worst and average cases, because the entire array needs to be iterated for every element.