Table of Contents
In this article , we will learn about Procurement Management , how does it works ,what is E -procurement, it’s tool and techniques that are used during the Procurement .
Many organizations employ various management techniques to carry out the efficient functioning of their departments. Procurement management is one such form of management, where goods and services are acquired from a different organization or firm.
What is Procurement?
Procurement is the process whereby companies purchase goods and services from various suppliers. These include everything from indirect goods like light bulbs, uniforms and
office supplies, to the direct goods used for manufacturing products.
Procurement also involves the purchase of temporary labor, energy, vehicle leases, and more. Companies negotiate discount contracts for some goods and services, and buy others on the spot. Procurement can be an important part of a company’s overall strategy for reducing costs.
The individuals or departments responsible for purchasing a company’s goods and services relied on various methods for doing so. The most basic included placing orders via telephone, fax, or mail.
All organizations deal with this form of management at some point in the life of their businesses. It is in the way the procurement is carried out and the planning of the process that will ensure the things run smoothly.
But with many other management techniques in use,
Is there any special reason to use this particular form of
management to acquire goods and services?
Yes, this is one of the frequent questions asked regarding procurement management. Procurement management is known to help an organization to save much of the money spent when purchasing goods and services from outside. It also has several other advantages.
How Does Procurement Management Works?
Following are the four main working areas of concerns when it comes to procurement management. The following points should be considered whenever procurement process is involved:
- Not all goods and services that a business requires need to be purchased from outside. It is for this reason that it is very essential to weigh the pros and cons of purchasing or renting these goods and services from outside.
- You would need to ask yourself whether it would in the long run be cost-effective and whether it is absolutely necessary.
- You would need to have a good idea of what you exactly require and then go on to consider various options and alternatives. Although there may be several suppliers, who provide the same goods and services, careful research would show you who of these suppliers will give you the best deal for your organization.
- You can definitely call for some kind of bidding for your requirement by these vendors and use a selection criterion to select the best provider.
- The next step typically would be to call for bids. During this stage, the different suppliers will provide you with quotes.
This stage is similar to that of choosing projects, as you would need to consider different criteria, apart from just the cost, to finally decide on which supplier you would want to go with.
- After the evaluation process, you would be able to select the best supplier. You would then need to move on to the step of discussing what should go into the contract.
Remember to mention all financing terms how you wish to make the payments, and so on, so as to prevent any confusion arising later on, as this contract will be binding.
Always remember that it is of utmost importance to maintain a good relationship with the supplier. This includes coming up with an agreement that both would find satisfactory. This helps the sustainability of your business as well as the supplier’s business.
These four simple steps would help you acquire your goods easily and quickly without much hassle, but always requires careful consideration at each stage.
Making the Process Work Efficiently
In order to ensure that everything goes well through to the end, you would have to keep track of the progress of the procurement. This would mean that you should keep checking on the suppliers in order to ensure that they are a biding by the terms of the contract and will be able to supply you with the goods and services by the deadline.
- Should there be any discrepancies or any issues, you should always let the supplier know by means of the method of communication decided on at the time of making the contract.
- The organization must always be willing and open to change. This is in respect of all changes required in order to ensure the efficiency of the process. These changes could be in the form of technological advancements and even changes to the workforce, among other changes.
- In terms of technology, any new equipment and machinery required to handle these goods may need to be purchased.Similarly, with regard to the workforce, you would need to employ workers, who are highly skilled and trained when it comes to dealing directly with suppliers.
- It is always best for an organization to have different teams within who are specialized in different fields. This would make procurement management even easier. Each team could then deal with the relevant areas of buying and will also have the expertise required. For example, those who have experience buying machinery may not have the same skill when it comes to getting particular services from another organization.
E-PROCUREMENT
Electronic procurement methods, generally referred to as e-procurement, potentially enable the procurement process to unfold in a faster, more efficient manner, and with fewer errors. These methods include electronic data interchange (EDI), online marketplaces or e-marketplaces, and various blends of the two.
- EDI deals more with the way information is communicated during procurement than it does with the act of linking buyers and suppliers.
- By definition, EDI is the electronic exchange of business information—purchase orders, invoices, bills of lading,
inventory data, and various types of confirmations— between organizations or trading partners in standardized
formats. - EDI also is used within individual organizations to transfer data between different divisions or departments,
such as finance, purchasing, and shipping. Two characteristics set EDI apart from other ways of exchanging information. - First, EDI only involves business-to-business transactions; individual consumers do not directly use EDI to purchase goods or services.
- Secondly, EDI involves transactions between computers or databases, not individuals. Therefore, individuals
sending e-mail messages or sharing files over a network does not constitute EDI. - EDI can occur point-to-point, where organizations communicate directly with one another over a private
network; via the Internet (also known as open EDI); and most commonly, via value-added networks (VANs),
which function like telephone lines by allowing for the transfer of information. - In the early 2000s, although many companies still relied on VANs, the Internet was playing a larger role in EDI.
It is possible for companies to translate the files used during EDI and send them to another company’s
computer system over the Internet, via e-mail, or file transfer protocol (FTP). - Because it is an open network and access is not terribly expensive, using the Internet for EDI can be more cost
effective for companies with limited means. - It has the potential to provide them with access to large companies who continue to rely on large,
traditional EDI systems. - The low cost associated with open EDI also means that more companies are likely to participate. This is
important because the level of value for participants often increases along with their number.
E-procurement tools and applications
Some e-procurement tools and applications include:
- Electronic systems to support traditional procurement
- EDI (electronic data interchange)
- ERP systems
- Internet as a support or complement to traditional procurement
- Electronic mail (e-mail)
- Web enabled EDI
- Extensible mark-up language (XML)
- World wide web (www)
- Internet tools and platforms that replace traditional procurement
Project management for procurement
It is usually divided into four major processes
- Planning,
- Selection,
- Administering
- Closing Procurements.
Internet Tools and Platforms
Some internet tools and platforms that replace traditional procurement include are as follows
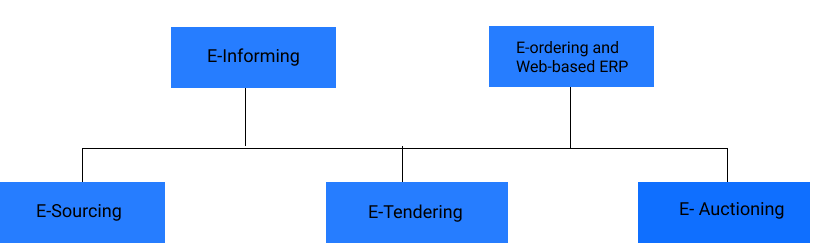
- E-sourcing
- E-tendering
- E- auctioning
- E-ordering and web-based ERP
- E-informing
Hope this article on Procurement Management is useful to you. Don’t forget to share your friends.