Table of Contents
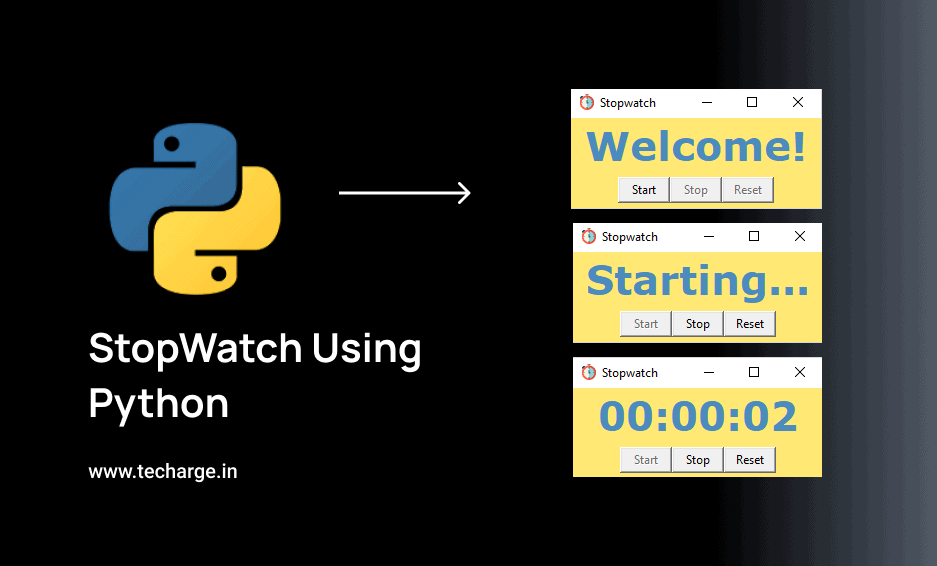
In this article, you’ll learn how can we create a StopWatch using Python.
For this, we need the tkinter module and Datetime module.
Tkinter is the standard GUI library for Python. Python when combined with Tkinter provides a fast and easy way to create GUI applications.
Datetime module supplies classes to work with date and time. These classes provide a number of functions to deal with dates, times, and time intervals.
To install tkinter module python, type the below command in your terminal–
pip install tkinter To install datetime module python, type the below command in your terminal–
pip install datetimeSource Code With Comments
# Python program to illustrate a stop watch
import tkinter as Tkinter
from datetime import datetime
counter=66600
running=False
def counter_label(label):
def count():
if running:
global counter
# To manage the initial delay.
if counter==66600:
display="Starting..."
else:
tt=datetime.fromtimestamp(counter)
string=tt.strftime("%H:%M:%S")
display=string
label['text']=display
label.after(1000, count)
counter+=1
# Triggering the start of the counter.
count()
# start function of the stopwatch
def Start(label):
global running
running=True
counter_label(label)
start['state']='disabled'
stop['state']='normal'
reset['state']='normal'
# Stop function of the stopwatch
def Stop():
global running
start['state']='normal'
stop['state']='disabled'
reset['state']='normal'
running=False
# Reset function of the stopwatch
def Reset(label):
global counter
counter=66600
# If rest is pressed after pressing stop.
if running == False:
reset['state']='disabled'
label['text']='Welcome!'
# If reset is pressed while the stopwatch is running.
else:
label['text']='Starting...'
root=Tkinter.Tk()
root.title("Stopwatch")
root.iconbitmap("stopwatch.ico")
root.configure(bg="#FFE873")
# Fixing the window size.
root.minsize(width=250,height=70)
label=Tkinter.Label(root,text="Welcome!",fg="#4B8BBE",bg="#FFE873",font="Verdana 30 bold")
label.pack()
f=Tkinter.Frame(root)
start=Tkinter.Button(f,text='Start',width=6,command=lambda:Start(label))
stop=Tkinter.Button(f,text='Stop',width=6,state='disabled',command=Stop)
reset=Tkinter.Button(f,text='Reset',width=6,state='disabled',command=lambda:Reset(label))
f.pack(anchor='center',pady=5)
start.pack(side="left")
stop.pack(side="left")
reset.pack(side="left")
root.mainloop()
Explanation of the Python stopwatch code
Key Components:
- Imports:
tkinter: For creating the GUI.datetime: For handling time calculations.
- Global Variables:
counter: Stores the elapsed time in milliseconds.running: A boolean flag to track whether the stopwatch is running.
- Functions:
counter_label:- Updates the displayed time on the label every second.
- Handles the initial “Starting…” message.
Start:- Initiates the stopwatch (sets
runningto True). - Enables/disables buttons appropriately.
- Initiates the stopwatch (sets
Stop:- Pauses the stopwatch (sets
runningto False). - Enables/disables buttons appropriately.
- Pauses the stopwatch (sets
Reset:- Resets the
counterand updates the display. - Handles button state changes based on the running status.
- Resets the
- GUI Setup:
- Creates the main window and sets its title and background color.
- Creates the label to display the time.
- Creates the “Start”, “Stop”, and “Reset” buttons.
- Arranges the elements on the window.
- Event Loop:
- Starts the
mainloopto handle user interactions (button clicks) and update the GUI.
- Starts the
Key Points:
- The
counter_labelfunction is the core of the timekeeping mechanism, usingafterto schedule updates. - The
Start,Stop, andResetfunctions manage the state of the stopwatch and the GUI elements. - The
datetimemodule is used to convert thecountervalue into a human-readable time format (HH:MM:SS).
Output of the StopWatch using Python
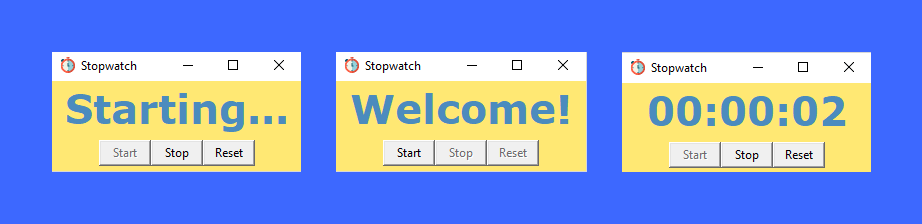
So, here is our StopWatch. Simple isn’t it?? This is how we have successfully done with the ‘StopWatch using Python’. I hope the ‘Tkinter and DateTime library is now more clear to you and don’t forget to try this code once!!
You can play around with the library, explore more features and even customize it further.
ThankYou Pythoner’s!!!
Check out more python projects
- PYTHON ROCK PAPER SCISSORS GAME
- CURRENCY CONVERTER IN PYTHON
- COVID-19 TRACKER APPLICATION USING PYTHON