Table of Contents
In this article, you’ll learn about Types of Cloud Computing, Cloud Computing Deployment Models, Cloud Computing Models and more.
Cloud computing is Internet-based computing in which resources is available over broad network access, these resources can be provisioned or released with minimum management efforts and service provider interaction.
Cloud computing is providing developers and IT departments with the ability to focus on what matters most and avoid undifferentiated work like procurement, maintenance, and capacity planning.
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid
- Community Cloud
Public Cloud
Public cloud is open to all to store and access information via the Internet using the pay-per-usage method.
The third-party service providers make resources and services available to their customers via Internet. Computing resources are managed and operated by the Cloud Service Provider (CSP).
Example: Amazon elastic compute cloud (EC2), IBM SmartCloud Enterprise, Microsoft, Google App Engine, Windows Azure Services Platform.
Private Cloud
Private cloud is also known as an internal cloud or corporate cloud. It is used by organizations to build and manage their own data centers internally or by the third party. It can be deployed using Opensource tools such as Openstack and Eucalyptus.
In this type of cloud, major control is over the infrastructure so security related issues are minimized.
Based on the location and management, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) divide private cloud into the following two parts-
- On-premise private cloud
- Outsourced private cloud
Hybrid Cloud is a combination of the public cloud and the private cloud. we can say:
Hybrid Cloud = Public Cloud + Private Cloud
A hybrid cloud is the combination of both private and public cloud. It is partially secure because the services which are running on the public cloud can be accessed by anyone, while the services which are running on a private cloud can be accessed only by the organization’s users.
The decision to run on private or public cloud usually depends on various parameters like sensitivity of data and applications, industry certifications and required standards, regulations, etc.
Example: Google Application Suite (Gmail, Google Apps, and Google Drive), Office 365 (MS Office on the Web and One Drive), Amazon Web Services.
Community Cloud
Community Cloud is somewhat similar to the Private cloud. In the private cloud, only one user or organization owns the cloud server. In Community Cloud, several companies with the same backgrounds share the cloud server.
If all organizations or companies have the same set of security protocols and performance requirements, and goals, this multi-tenant architecture can help them save cost and boost efficiency. This model can be used in the case of project development, implementation, and maintenance.
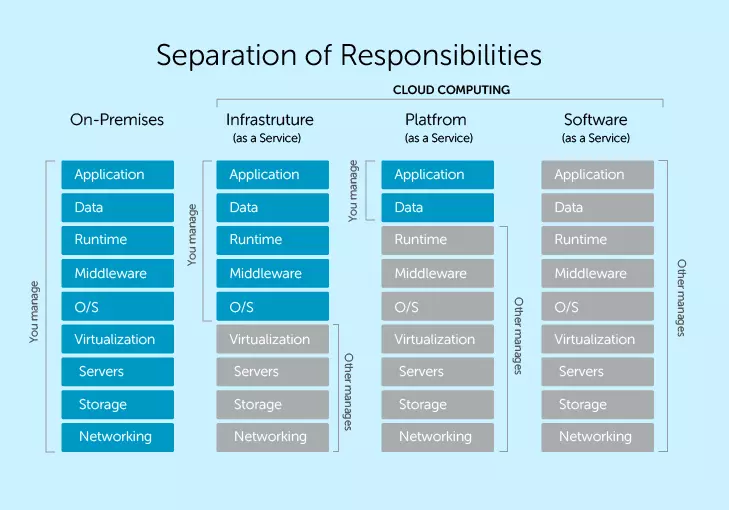
Cloud Computing Models
There are three main models for cloud computing. Each model represents a different part of the cloud computing stack.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Provide building blocks for cloud IT
- Provides networking, computers, data storage space
- Highest level of flexibility
- Easy parallel with traditional on-premises IT
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Removes the need for your organization to manage the underlying infrastructure
- Focus on the deployment and management of your applications
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Completed product that is run and managed by the service provide
Example of Cloud Computing Types
Infrastructure as a Service
- Amazon EC2 (on AWS)
- GCP, Azure, Rackspace, Digital Ocean, Linode .
Platform as a Service
Software as a Service
- Many AWS services (ex: Rekognition for Machine Learning)
- Google Apps (Gmail), Dropbox, Zoom
