Table of Contents
In this article, you’ll learn about what is ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network), ISDN Interface, ISDN Services, Principle of ISDN and more.
What is ISDN?
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the digitalized circuits of the public switched telephone network.
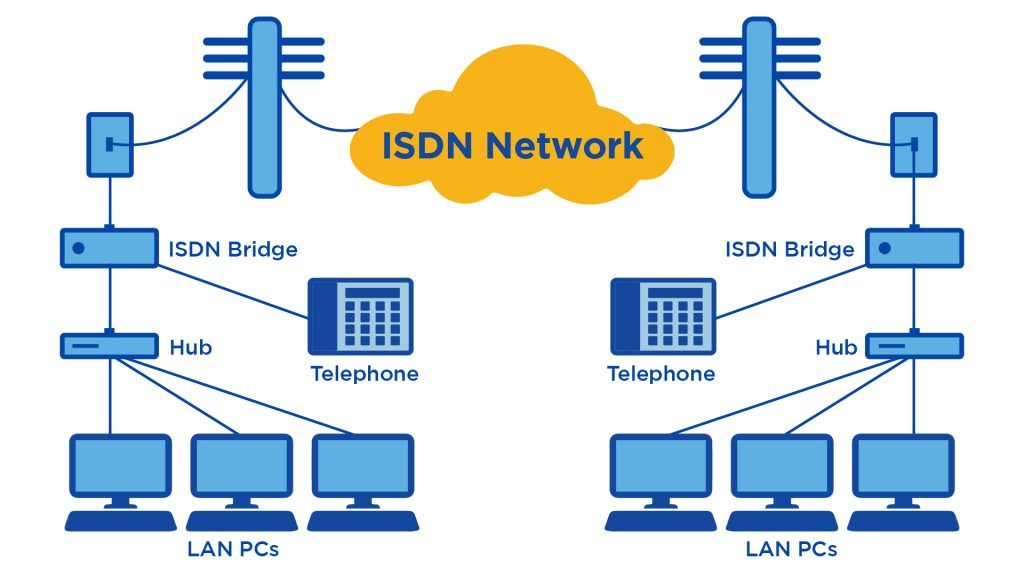
Before, ISDN the telephone system seen as a way to transmit voice with some special services available for data. The main feature of ISDN is that it can integrate speech and data on the some lines, which were not available in the classic telephone System.
There are two types of channel that are found within ISDN:
- B or Bearer channels: The bearer channels are used to carry the payload data which may be voice and / or data
- D or Delta channels: The D channels are intended for signalling and control, although it may also be used for data under some circumstances.
Additionally there are two levels of ISDN access that may be provided. These are known as BRI and PRI.
ISDN supports a variety of services. A few of them are listed below −
- Voice calls
- Videotext
- Facsimile
- Electronic Mail
- Database access
- Data transmission and voice
- Connection to internet
- Electronic Fund transfer
- Teletext
- Image and graphics exchange
- Document storage and transfer
- Audio and Video Conferencing
- Automatic alarm services to fire stations, police, medical etc.
ISDN Interface
There are following ISDN interface are:
- Basic Rate Interface (BRI)
There are two data-bearing channels (‘B’ channels) and one signaling channel (‘D’ channel) in BRI to initiate connections. The B channels operate at a maximum of 64 Kbps while the D channel operates at a maximum of 16 Kbps. The two channels are independent of each other. For example, one channel is used as a TCP/IP connection to a location while the other channel is used to send a fax to a remote location. In iSeries ISDN supports basic rate interface (BRl). The basic rate interface (BRl) specifies a digital pipe consisting two B channels of 64 Kbps each and one D channel of 16 Kbps. This equals a speed of 144 Kbps. In addition, the BRl service itself requires an operating overhead of 48 Kbps. Therefore a digital pipe of 192 Kbps is required. - Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
Primary Rate Interface service consists of a D channel and either 23 or 30 B channels depending on the country you are in. PRI is not supported on the iSeries. A digital pipe with 23 B channels and one 64 Kbps D channel is present in the usual Primary Rate Interface (PRI). Twenty-three B channels of 64 Kbps each and one D channel of 64 Kbps equals 1.536 Mbps. The PRI service uses 8 Kbps of overhead also. Therefore PRI requires a digital pipe of 1.544 Mbps. - Broadband-ISDN (B-ISDN)
Narrowband ISDN has been designed to operate over the current communications infrastructure, which is heavily dependent on the copper cable however B-ISDN relies mainly on the evolution of fiber optics. According to CCITT B-ISDN is best described as ‘a service requiring transmission channels capable of supporting rates greater than the primary rate.
ISDN Services
ISDN provides a fully integrated digital service to users. These services fall into 3 categories- bearer services, teleservices and supplementary services.
- Bearer Services
Transfer of information (voice, data and video) between users without the network manipulating the content of that information is provided by the bearer network. There is no need for the network to process the information and therefore does not change the content. Bearer services belong to the first three layers of the OSI model. They are well defined in the ISDN standard. They can be provided using circuit-switched, packet-switched, frame-switched, or cell-switched networks. - Teleservices
In this the network may change or process the contents of the data. These services corresponds to layers 4-7 of the OSI model. Teleservices relay on the facilities of the bearer services and are designed to accommodate complex user needs. The user need not to be aware of the details of the process. Teleservices include telephony, teletex, telefax, videotex, telex and teleconferencing. Though the ISDN defines these services by name yet they have not yet become standards. - Supplementary Service
Additional functionality to the bearer services and teleservices are provided by supplementary services. Reverse charging, call waiting, and message handling are examples of supplementary services which are all familiar with today’s telephone company services.
Principle of ISDN
The ISDN works based on the standards defined by ITU-T (formerly CCITT). The Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) coordinates standards for telecommunications on behalf of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is based in Geneva, Switzerland. The various principles of ISDN as per ITU-T recommendation are:
- To support switched and non-switched applications
- To support voice and non-voice applications
- Reliance on 64-kbps connections
- Intelligence in the network
- Layered protocol architecture
- Variety of configurations
Advantages of ISDN
ISDN is a telephone network-based infrastructure, which enables the transmission of both voice and data simultaneously. There are many advantages of ISDN such as
- As the services are digital, there is less chance for errors.
- The connection is faster.
- The bandwidth is higher.
- Voice, data and video − all of these can be sent over a single ISDN line.
Disadvantages of ISDN
The disadvantage of ISDN is that it requires specialized digital services and is costlier.
However, the advent of ISDN has brought great advancement in communications. Multiple transmissions with greater speed are being achieved with higher levels of accuracy.